Best NMN Supplements from Japan: Benefits, Risks, and How to Choose

This article examines the anti-aging benefits and side effects of NMN (β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), a Vitamin B3 derivative. Discover tips for selecting NMN products and explore leading Japanese brands to find the perfect option for your needs.
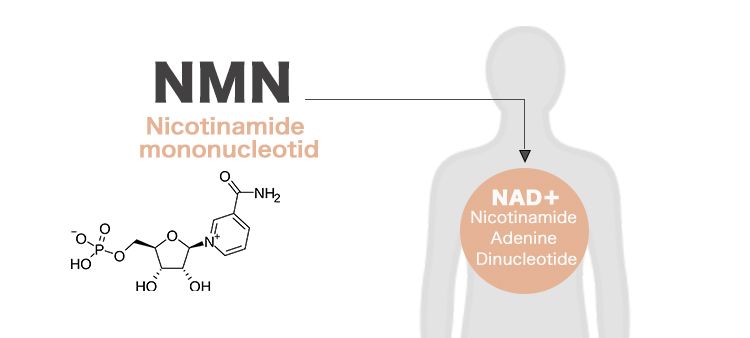
What is NMN (β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)?
NMN (β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is a naturally occurring molecule that is a derivative of Vitamin B3. It is involved in the synthesis of NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a crucial coenzyme vital for cellular energy metabolism and maintaining DNA repair. As we age, NAD+ levels decline, which is thought to be related to various physiological and health issues associated with aging.
What are the benefits of NMN?
The primary function of NMN is to increase NAD+ levels, thus promoting better cellular function and energy metabolism. Research suggests that NMN may have the following benefits:
- Anti-aging: NMN can help repair DNA damage, support cellular health, and may help slow the aging process.
- Improved Metabolism: Enhances insulin sensitivity, supports healthy metabolism, and may benefit metabolic diseases like diabetes.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function: By supporting brain cell energy metabolism, it may improve memory and cognitive function.
- Improved Cardiovascular Health: NMN might protect the cardiovascular system by improving vascular function and lowering cholesterol levels.
How was NMN discovered?
Research into NMN (β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) as an important molecule began in the late 20th and early 21st centuries, during which scientists started exploring biochemical pathways related to aging. At that time, various researchers, including those from Harvard University, discovered that supplementing cells with NMN could increase NAD+ levels. This significant finding dramatically increased interest and understanding of NMN's potential applications in anti-aging, physiological health, and metabolic regulation.
In this context, the research team led by David A. Sinclair revealed how NMN could effectively function in slowing aging and promoting long-term health. Subsequently, Shin-ichiro Imai and his team performed studies in mouse models that further demonstrated NMN's potential for improving metabolic function. Kristopher F. Mills' research showed the effects of NMN supplementation in enhancing metabolic health and possibly extending lifespan, while Jun Yoshino focused on NMN's impact on energy metabolism in the context of aging and metabolic diseases.
These research findings have been published in academic journals such as Cell Metabolism, Nature Communications, and Journal of Biological Chemistry. These studies not only propelled the scientific community's exploration of NMN's applications but also underscore NMN's growing potential in health and longevity as technology advances and understanding of human aging mechanisms deepens. For individuals interested in exploring these studies further, using academic databases such as PubMed or Google Scholar to search for relevant researchers and keywords like "NMN" and "NAD+ metabolism" can provide more detailed information and further research content.
Can NMN be consumed through food?
NMN (β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) can be obtained through certain foods, but its content is usually low, so consuming these foods may not significantly increase NMN levels in the body.
Here are some foods that contain NMN or its precursors:
- Vegetables: Green vegetables such as broccoli and cabbage contain some amount of NMN.
- Fruits: Fruits like avocados and tomatoes are also thought to contain NMN.
- Meat: Small amounts of NMN can be found in meats, especially in organ meat.
- Seafood: Seafood like shrimp can also contain NMN.
- Fermented Foods: Some fermented foods may contain precursor substances to NMN.
Although these foods contain NMN, the dosage obtained through everyday diet is relatively low, which is why some people choose to increase NMN intake through dietary supplements. However, it is recommended to consult with medical or nutrition professionals to evaluate the appropriate dosage and safety before considering using supplements.
Are there any side effects of taking NMN?
So far, NMN has not been widely reported to have noticeable side effects. However, since research is ongoing, more data is needed to support the safety and potential side effects of long-term use. Here are some research reports on NMN safety and benefits from recent years, and if needed, these can be searched for more detailed information.
- Harvard Medical School and Metro International Biotech (February 9, 2022): Daily intake of 1000mg or 2000mg of NMN is safe for middle-aged and elderly people without side effects and significantly increases NAD+ levels.
- Japanese Clinical Trial (2020): 10 healthy men took 100 to 500 mg of NMN, showing no side effects and only minor changes in blood markers.
- Washington University (April 22, 2021): For pre-diabetic women, 250mg of NMN improved metabolism and muscle function with no side effects.
- Research Square (June 9, 2021): Men over 65 took 250mg of NMN for 12 weeks, enhancing NAD+ levels and muscle performance without side effects.
- Doshisha University, Japan (June 22, 2022): NMN reversed aging signs in elderly women.
Who should avoid taking NMN?
Pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and patients with chronic diseases (e.g., liver disease, kidney disease) should consult a doctor before consumption. Additionally, the safety for minors has not been established, so usage is not recommended.
How to choose NMN products?
- Check the NMN content per capsule based on your goals
Understand how much NMN is in each dietary supplement capsule. Focusing on NMN content rather than purity is a more effective approach, with a recommended daily intake of about 200mg. - Carefully review the ingredient list
With a wide range of NMN supplements available, their quality varies, so it is crucial to choose carefully. Ensure that the ingredient list on the product packaging clearly states the NMN content. - Pay attention to GMP certification
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) certification is an international standard for quality management of manufacturing facilities. Choosing NMN supplements produced in GMP-certified facilities ensures high standards in manufacturing processes and quality management. - Consider price and ease of consumption
Long-term consumption is necessary for NMN supplements to be effective, so consider their convenience for sustained use. Pay attention to the cost per capsule and the size of the supplement to ensure it doesn't cause stress when taking. Choosing products that require only one pill a day makes long-term consumption more convenient.
Recommended NMN Products Made in Japan ▼
In Japan, NMN as a dietary supplement is regulated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and the Consumer Affairs Agency to ensure safety and effectiveness. As dietary supplements, NMN products do not need to undergo the approval process of clinical trials like pharmaceuticals, but manufacturers must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and clearly list ingredients and usage guidelines on product labels so consumers can properly understand and use the products. Click on the products for more detailed introductions!

![[Nutritional Supplement] Supplement NMN20000 80 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/skus/7775919/87d07b7b575839f05763d1735e37f4f3.jpg?d=0x0)













![[Set of 3] NMN15000mg 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9045341/1a77f8dd14fb7b2980f75f3211b1a633.jpg?d=0x0)




![[Set of 5] NMN15000mg 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9045342/85f75e0cce313d7eb233cbae9759bac8.jpg?d=0x0)



![[Set of 2] Meiji Pharmaceutical NMN 10000 Supreme MSNS 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9049141/6af9fd49d64da0aa2fca4ee3f5ea0d97.png?d=0x0)
![[Set of 3] Meiji Pharmaceutical NMN 10000 Supreme MSNS 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9049142/592f54cd2f04a775191e4a26e8c51640.png?d=0x0)

![[Set of 2] Wellness Life Science NMN25000 120 Capsules](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9049139/094ac57c7fd428b9614e001f3b9b003c.png?d=0x0)
![[Set of 3] Wellness Life Science NMN25000 120 Capsules](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9049140/e055c4dab942553bb4e0850022c9eea4.png?d=0x0)
![[Set of 2] NMN PURE 900 Plus (60 capsules) 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9046573/108cab4937d517515fa74a02a6745434.png?d=0x0)
![[Set of 2] Meiji Pharmaceutical NMN 10000plus Supreme MSNS 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9049143/524981582308036f606ca210a4ffe8d7.png?d=0x0)
![[Set of 3] NMN PURE 900 Plus (60 capsules) 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9046574/d10d8e9250dc6cc60e4d4b5ccc5cf0ce.png?d=0x0)
![[Set of 3] Meiji Pharmaceutical NMN 10000plus Supreme MSNS 60 tablets](https://image.dokodemo.world/catalog-skus/9049144/7fce01f1d1a169fd46e27f4424da16d5.png?d=0x0)





